What Does Newton's Second Law Describe
Newtons laws of motion. Newtons second law works as a way to describe the motion of everything in a quantum mechanical system as long as the particles are not moving near the speed of light.
Newtons second law is often stated as Fma which means the force F acting on an object is equal to the mass m of an object times its acceleration a.

. Newtons second law can be used to describe the acceleration of an object based on total force applied and the mass of the object. Force The acceleration of an object depends on the mass of the object and the amount of force applied. Google Classroom Facebook Twitter.
The equation is commonly written as Fma. For an object at rest the applied force produces acceleration in the object and makes the object move in the direction of applied force. Newtons second law describes the motion of an object when an unbalanced force acts on the object.
Simply put the more force applied to an object the faster it will accelerate. What is Newtons first law. A What does Newtons second law of motion describe.
Why is it that the internal forces of the system have no effect on motion. Newtons second law of motion describes the relationship between an objects mass and the amount of force needed to accelerate it. F net ma.
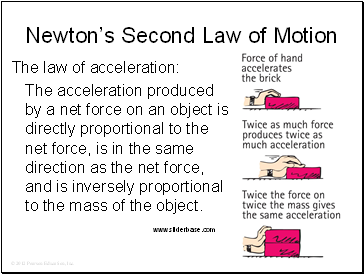
Newtons 2nd law states that the acceleration of an object as produced by a net force is directly proportional to the magnitude of the net force in the same direction as the net force and inversely proportional to the objects mass. Force mass acceleration Explanation. More on Newtons first law of motion.
Newtons second law of motion describes that when a force is applied to an object it produces acceleration in the object ie rate of change of velocity. For an object which is already in motion the direction of the applied force matters to determine. What is newtons 2nd law of motion.
Applying Newtons first law of motion. The second law states that the acceleration of an object is dependent upon two variables - the net force acting upon the object and the. Force on the mass is zero and as Newtons first law tells us there will be no acceleration of the mass If one mass is heavier than the other then the masses may accelerate one moving upward and the other down.
When an object is moving. Newtons second law of motion pertains to the behavior of objects for which all existing forces. A net force changes the velocity of an object by changing either its speed or its direction.
In equation form Newtons second law of motion is a. Weight Newtons second law as an equation. Newtons 2nd law states that if a force is put on an object then the object will move in the oppisite direction of the force no thats the third law.
The acceleration of an object equals the net force on the object divide by its mass. Newtons second law of motion pertains to the behavior of objects for which all existing forces are not balanced. B A toboggan loaded with students total weight w slides down a snow-covered slope.
Newtons second law of motion states that the acceleration of a system is directly proportional to and in the same direction as the net external force acting on the system and inversely proportional to its mass. A change in velocity is called an acceleration. Therefore an object moving in a circle is undergoing an acceleration.
In the simplest case a force applied to an object at rest causes it to accelerate in the direction of the force. Newtons second law states that the unbalanced force acting on an object is equal to the mass of the object times its acceleration. Review your understanding of Newtons second law in this free article aligned to NGSS standards.
The second law of motion by Newton states that an objected acted upon by the force will undergo acceleration in such a way that the force equals the mass multiplied by acceleration. Newtons second law says that when a constant force acts on a massive body it causes it to accelerate ie to change its velocity at a constant rate. In the simplest case a force applied to an object at rest causes it to accelerate in the direction of the force.
Newtons first law of motion introduction. Mathematically this is represented as Fma. Newtons second law describes the relationship among force mass and acceleration.
Newtons second law tells us that in this case there must be a net force on each mass. His second law defines a force to be equal to change in momentum mass times velocity per change in time. Newtons Second Law.
Newtons second law of motion describes the relationship between force mass and acceleration. Newtons Second Law explains it this way. This means the more mass an object has the more force you need to.
If the units of force are newtons the units of mass are kilograms and the units for acceleration are ms2 True or False. Newtons Second law of motion. The hill slopes at a constant angle α and the toboggan is so appropriately waxed so that there is virtually no friction.
An example of the second law of motion is when you are riding a bike. Newtons second law can be describe by this equation. These days we usually write it as Force mass x acceleration.
Newtons second law says that when a constant force acts on a massive body it causes it to accelerate ie to change its velocity at a constant rate. Newtons second law describes precisely how much an object will accelerate for a given net force. Your bike is the mass and our leg muscles pushing on the pedals of your bike are the force.
2nd Law Of Motion Forces T3 S T E A M

Cbse Class 9 Newton S Second Law Of Motion In Hindi Offered By Unacademy
0 Response to "What Does Newton's Second Law Describe"
Post a Comment